Staphylococcus aureus , E coli and Klebsiella penumoniae on growth on various media 328 Urine of UTI patient under the Microscope 155 Last updated on May 30th, 21 If you observe a probable fungus in the culture plate, colony characteristics are first assessed to determine the broad group of the isolateOnce the initial observations are made, the following microscopic criteria are used to make a genus/species identification of the fungal isolateThe bladelike plates under the pileus on which the spores are produced are called gills or lamella;
Club Fungi
Club fungi under microscope
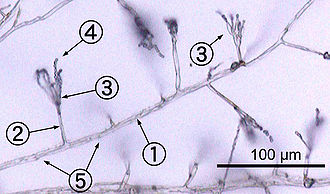
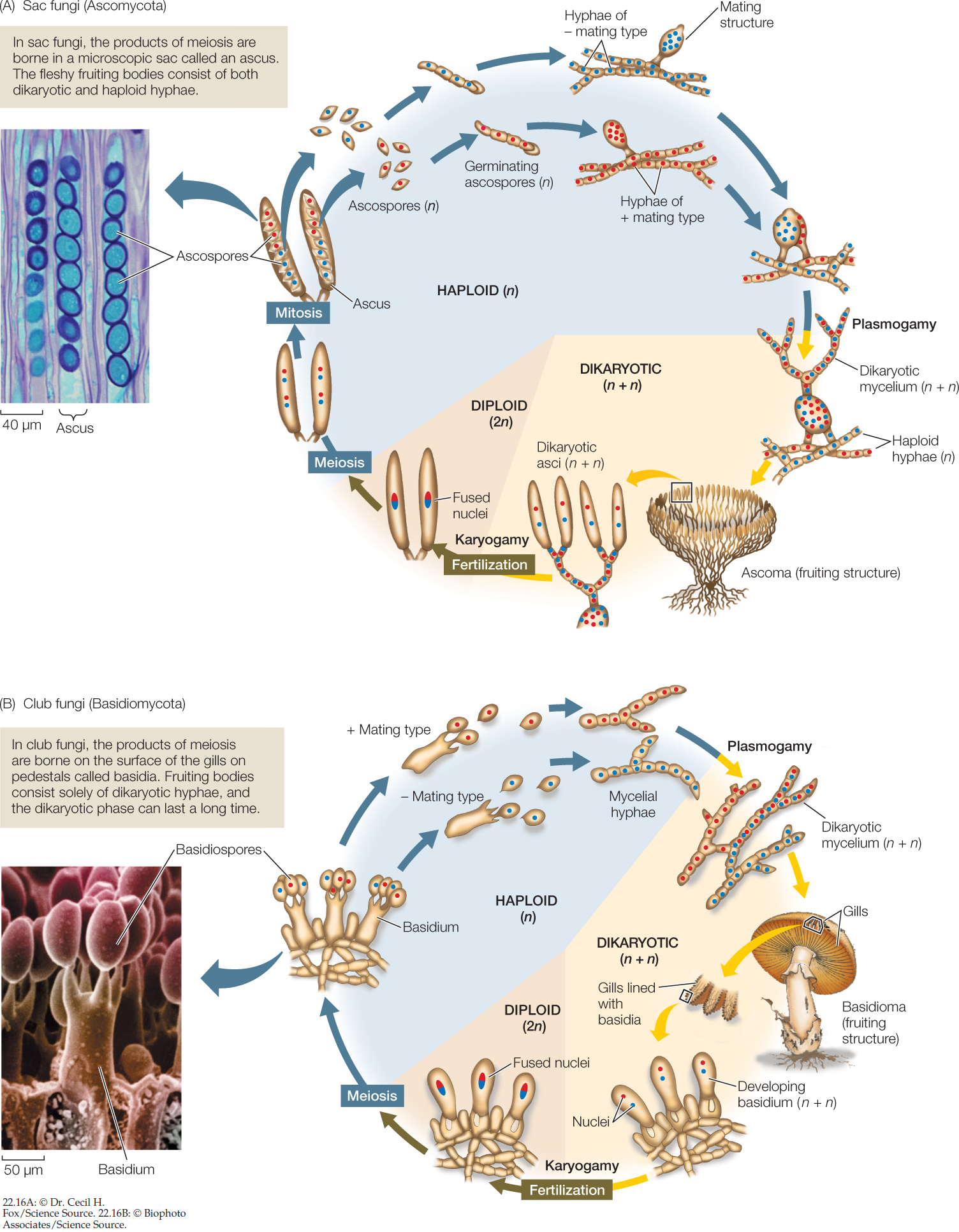
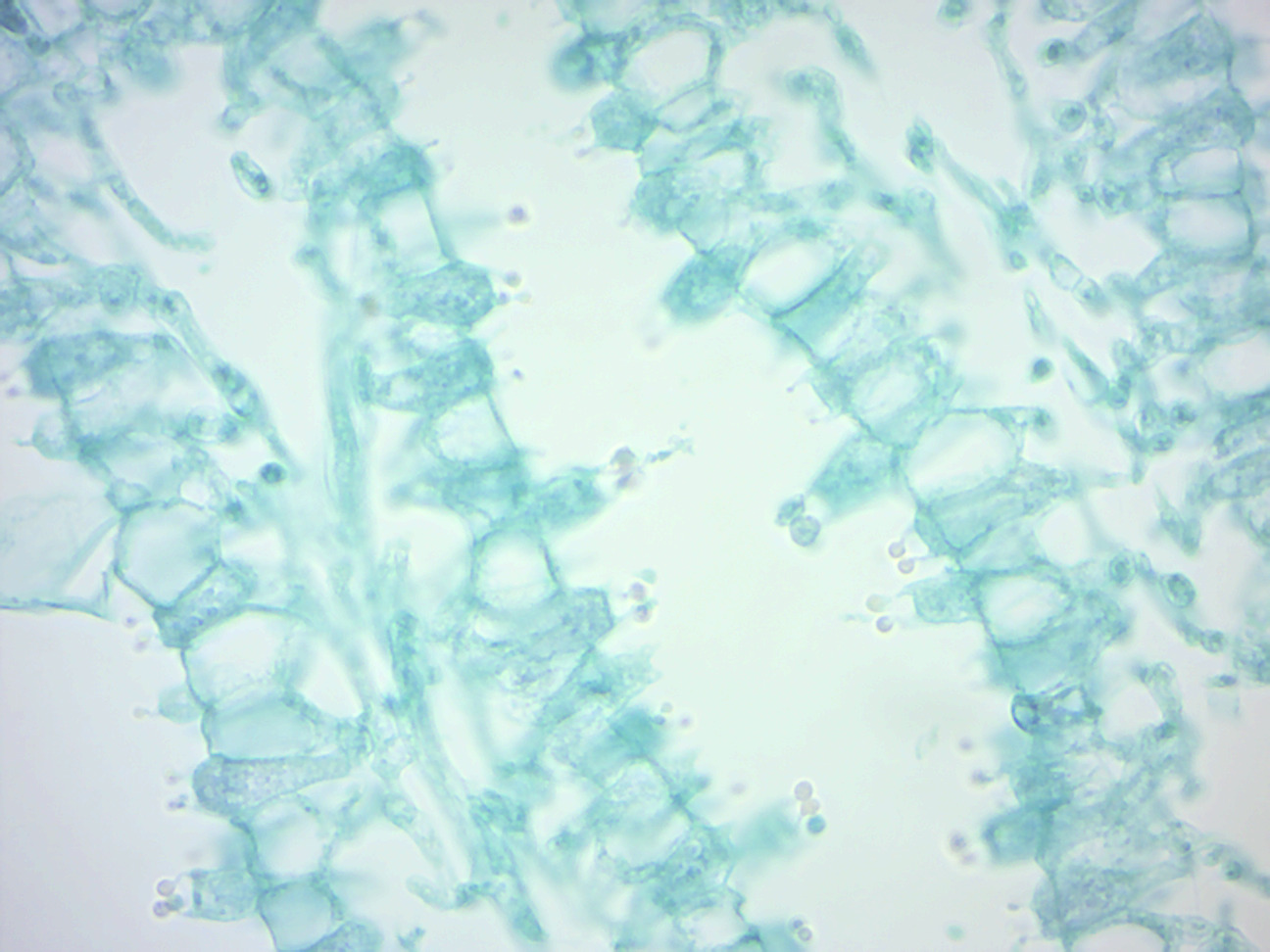
Club fungi under microscope-Hyphae are the microscopic tubular filaments that make up the main structure which is mostly The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hypha




Fungi Microbiology
Most fungi cannot with certainty be identified with the naked eye, and need to be examined under the microscope You will need a microscope providing magnifications from 10 to 1000, a graticule (scale) in one eyepiece, some stains, pipettes, a razor blade or a sharp knife, some tweezers, microscope slides, cover slips and immersion oil (for the high powered microscope objectives)The fungi comprise a diverse group of organisms that are heterotrophic and typically saprozoic In addition to the wellknown macroscopic fungi (such as mushrooms and molds), many unicellular yeasts and spores of macroscopic fungi are microscopic For this reason, fungi are included within the field of microbiology44 Aspergillus Aspergillus is a genus consisting of a few hundred species of mold found in various climates worldwideAspergillus was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli Viewing the fungi under a microscope, Micheli was reminded of the shape of an aspergillum (holy water sprinkler), from Latin spargere (to sprinkle), and named the genus
The simplest of the fungi, the chytrids are microscopic and found in freshwater, mud, soil and sometimes the rumen Zygomycota (club fungi) Basidiomycetes also Describe the morphology and draw an example of each colony in the results section View the plates under the dissecting microscope Make a sketch and try to identify the hyphaeScanning electron microscope (SEM) micrograph of the surface of cherry plum (Prunus cerasifera) tree leaf, showing cellular structure of leaf and particles of an unknown fungus or other coating flaking off of the leaf, at a magnification of 800x, 16Georgia Regents University (Formerly Augusta State University) Bio 1108 Lab Practical #1 (Protists, Fungi and Microscope) Terms in this set (38) Mechanical Stage club fungiform basidiospores on club shaped structures called basidia mushrooms, puffbals, Some images used in this set are licensed under the Creative Commons through
Penicillium glaucum , mold that is used in the making of some types of blue cheese and aspergillus glaucus is a filamentous fungus fungi microscope stock illustrations Aspergillus clavatus viewed under the microscope, ascomycete fungiThe fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular,The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium ), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hypha The basidia, which are the reproductive organs of these fungi, are often contained within the familiar mushroom, commonly seen in fields




Fungus Wikipedia



Fungus Microscopic View Of S Free Stock Photos Rgbstock Free Stock Images Hisks February 13 10 19
Needed fungi and examine Draw what you see under the microscope once you have found the fungi List and label the required characteristics of the particular fungus This typically included sperm/egg Once you have looked at all the prepared slides, Lab 10 Fungi, Part 2 The Molds Molds are multinucleated, filamentous fungi composed of hyphae A hypha is a branching, tubular structure from 210 µm in diameter and is usually divided into celllike units by crosswalls called septa The total mass ofIn the 1900s the microscopic features became more important so, while all of the features mentioned below are still very useful for identification, their role in classification is often much reduced Of prime importance is the type of fruiting body (eg mushroom, puffball, cup fungus, polypore, etc (SEE TYPES OF FUNGI SECTION)




29 Basidiomycetes Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images
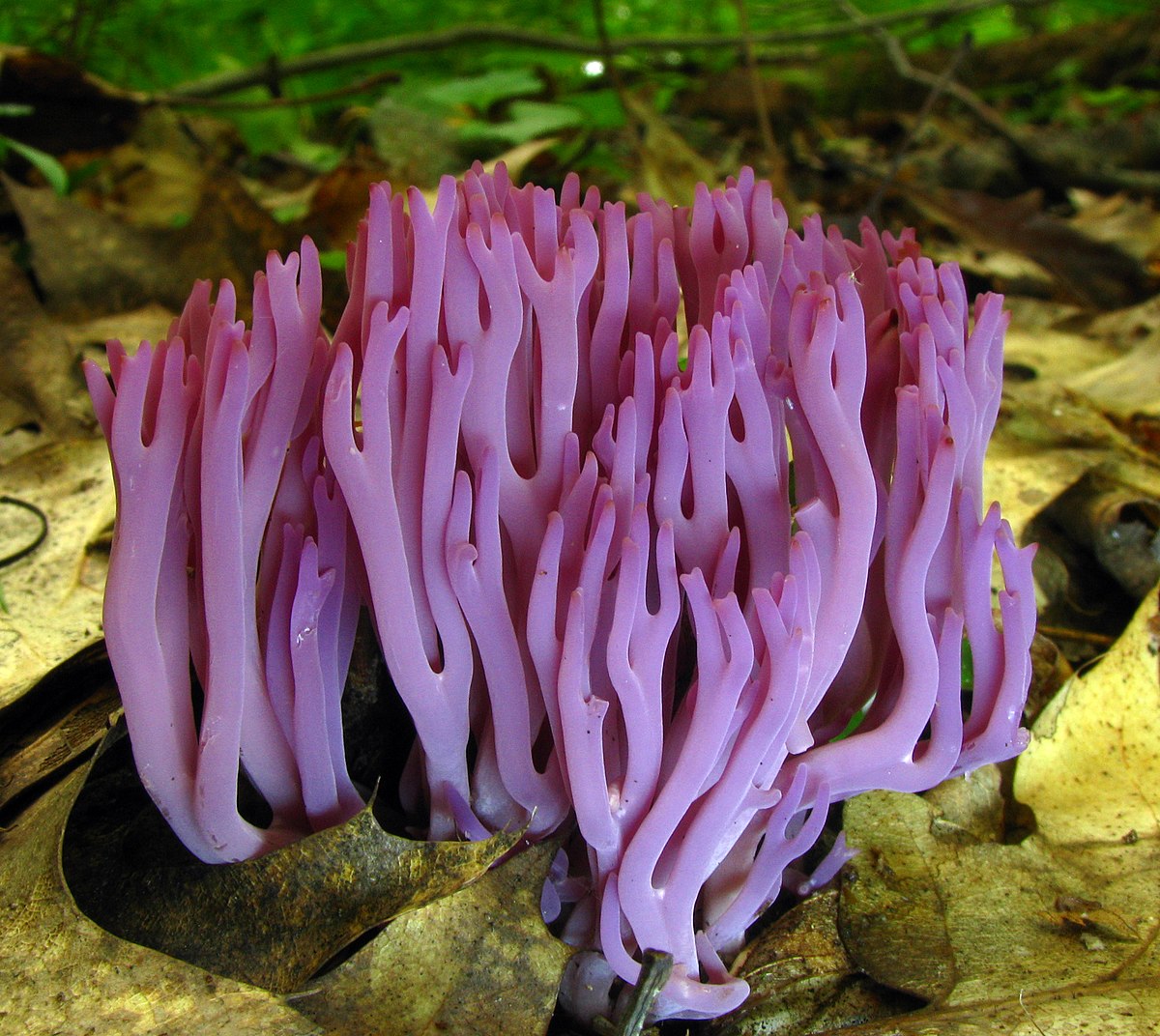




Club Fungus Wiktionary
The three primary components of a microscope to examine psilocybin cubensis spores under microscope lab equipment are the head, the base, and the arm The head is the "body" of the microscope (and is sometimes referred to as such in certain documents and instructions, so keep that in mind) The head is responsible for carrying opticalThe stem is called a stipe ;Mushrooms under the Microscope Mushrooms, also known as fungi or toadstools, are the sporebearing fruiting body of a fungus The mushroom typically grows above ground or on top of its food source (on a log, or out the side of a mossy tree) A mushroom has a stem and a cap along with gills




Basidiomycetes Club Fungi Instruments Direct



Using A Microscope To Study Mushrooms Mushroomexpert Com
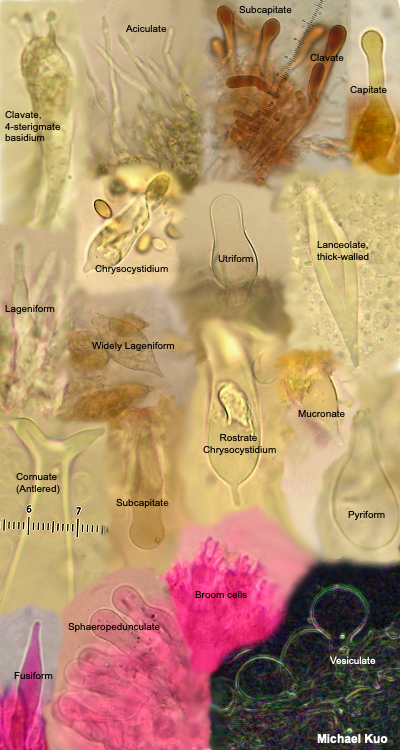
Use the lowest magnification on a compound microscope and move the stage so that the entire fungus passes through the field of view You will need to focus up and down according to the size of the subject in view It is possible to use the same process to look at the number of spores on the collection's basidiaFirst a word on names fungi are not plants so their parts have fungusspecific terms The cap, as in mushroomshaped fungi, is also referred to as a pileus;Basidiomycota The Club Fungi The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium ), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hypha The basidia, which are the reproductive organs of these fungi, are often contained within the familiar




Fungi Microbiology




Fluorescence Microscopy Journal Club Bruker
The clavarioid fungi are a group of fungi in the Basidiomycota typically having erect, simple or branched basidiocarps (fruit bodies) that are formed on the ground, on decaying vegetation, or on dead wood They are colloquially called club fungi and coral fungi Originally such fungi were referred to the genus Clavaria ("clavarioid" means Clavarialike), but it is now known that(fungi under microscope) Of course, all the fungal strands by now may not all be joined up to form a huge single organism – connections in the microscopic fungal strands in the soil may have broken as it grew outwards from the original germination point in the forest 1500 years ago But it's a pity to spoil1 The visible fungi composed of densely packed hyphae that typically grow out the substrate 2 Reproductive structure of fungi that produces spores



Club Fungi




Fungi Microbiology
Nail Fungus Under Microscope Other Symptoms Can Include • Brittle, split, cracked, ragged, or falling apart nails • Changes or distortion of the shape • Lifting or detachment of the nail from the nail bed • Thickening of the nails, making them tough to cut • Nasty, foul odor • Yellow, brown or white discoloration of the nailFungus under Microscope Fungal structures Aspergillus The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hypha This group also includes shelf fungus, which cling to the bark of trees like small shelves



Mushrooms Under The Microscope



Fungus Wikipedia
This multiplication of yeast cells is usually rapidly occurring, and thus easy to observe on a microscope Of course, the various parts of a yeast cell can also be identified by using a higher powered microscope, or a fluorescent microscope For this purpose, the yeast almost always needs to be dyed in order for the details to become clearly visible Fungal spores are haploid cells that are produced by meiosis and are used to disperse the fungus When they land in a suitable location they germinate and grow Yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae The image below was taken by Dr Tammy Oliver using a Leica microscope with a digital camera attachedClub Fungi Other Funguslike and observe with the compound microscope Look for the basidia and spores Examine a prepared slide showing the crosssection of the the common name for members of the genus Boletus and other related genera that look like gill mushrooms but have pores under the cap instead of gills Like the



Teaching The Fungal Tree Of Life Home




Chapter 24 Fungi Insert Photo Here Representing Chapter
Microscopic fungi are eukaryotic, heterotrophic microorganisms that fail to show any cellular differentiation into true tissues like root, stem or leaf and in which vascular system is absent B Characteristics of Fungi The major distinguishing characteristics of fungi are given below Fungi have been shooting their spores all over a table in professor Fernando Tenjo's classroom His students gather them up and joke about how "adorable" and "cute" the little reproductive necessities look under the microscope Few people would use those same words to describe the fungi over by the windowYou could buy a new microscope, of course You can probably find new microscopes online that meet the requirements above for under $400 at the time of this writing (19) However, and this is a big however, you cannot find a good new microscope for that price



Clavulina Rugosa Wrinkled Club Fungus



Basidiomycota
Microscope Bacteria Identification Upon viewing the bacteria under the microscope, you will be able to identify the bacteria based on a wide variety of physical characteristics This mainly involves looking at their shape and size There are a wide variety of different shapes, yet the three main types are cocci, bacilli, and spiralMushrooms are the largest group of the fungi Mushrooms belong to the club fungus group due to their clublike structures Mushrooms have 4 basic parts The top of the mushroom, the umbrella or the part that grows above the ground is called the CAP Under the cap are the GILLS Inside the gills are the sporesTo study fungal spores, basidia, cystidia, sphaerocysts and other tiny features of fungi you will need a microscope capable of at least x 400 magnification Ideally, go for a microscope with a maximum magnification of x 1000, but to obtain reasonably clear images at such high magnification it should have an oil immersion lens



Experiment 24 General Medical Microbiology Lab
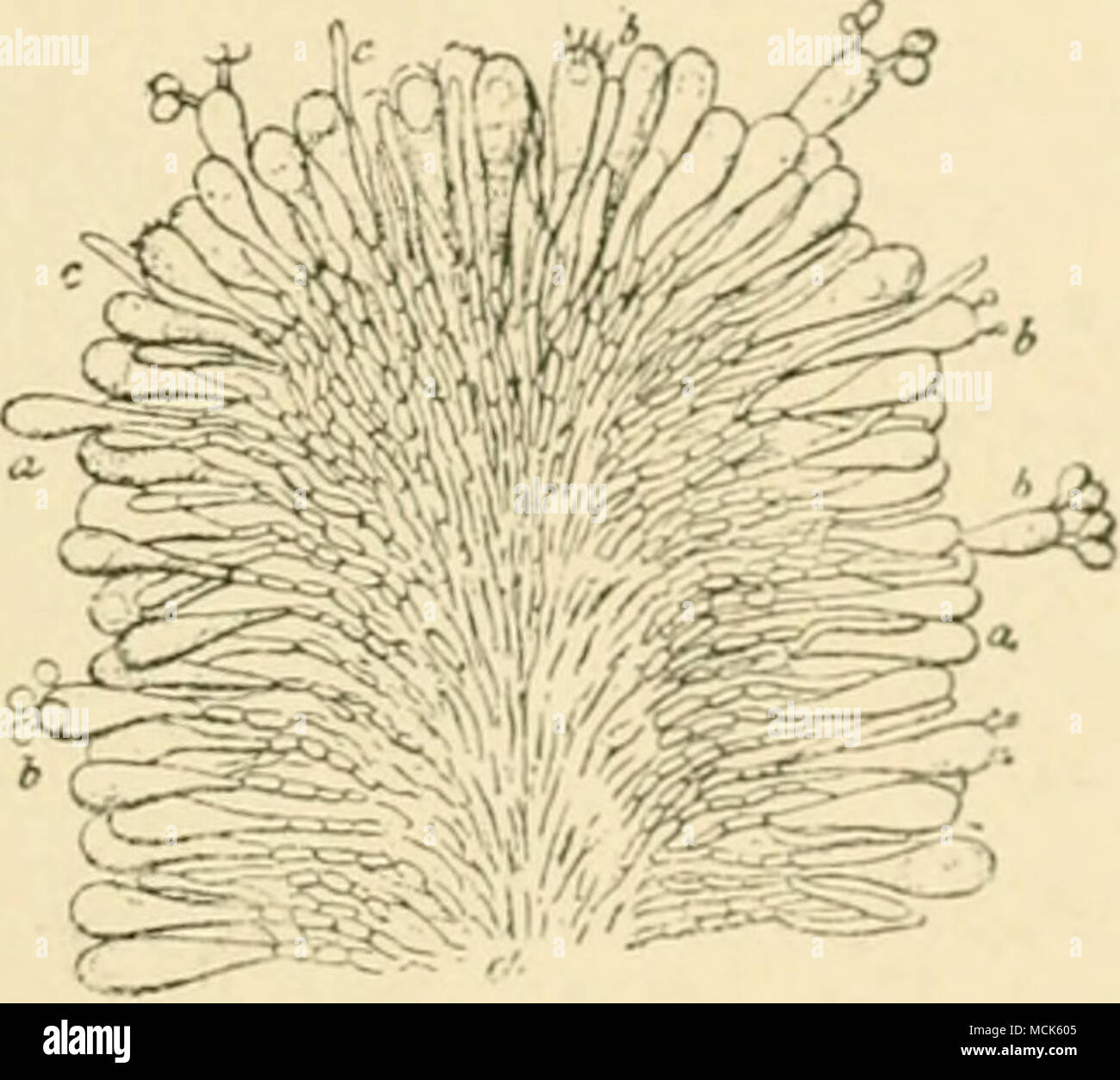



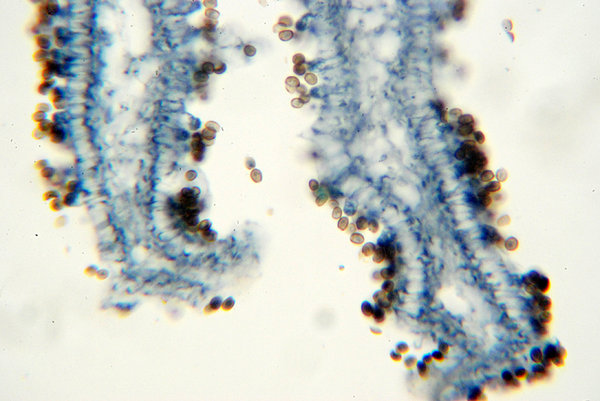
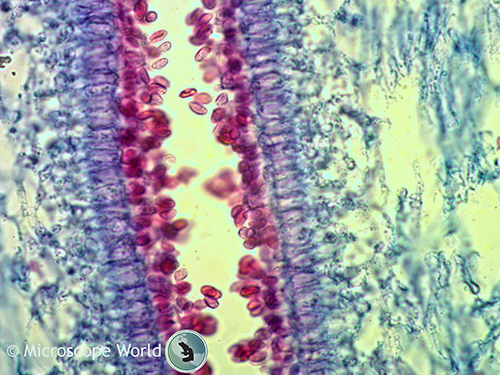
Fig 2s Quot Ar Uricus Meluvx Section Through A Lamella The Hyphae Forming The Subsfcmce Of The Lamella Are Mucli Branched And Send Twigs Outwards Which End In Club Shaped Basidia
Course Content Expand All Lesson 1 Introduction to the Microscope Lesson 2 Sample Preparation Lesson 3 Morphology of Bacteria Lesson 4 Morphology of Fungi Lesson 5 Morphology of Algae, Protozoa & Nematodes Lesson 6 Morphology of Other Materials in Soil Lesson 7 Quantification Counting OrganismsThe growth looks fuzzy, powdery, or like a spiderweb Lift some compost with the sample on top, and and prepare a slide with cover slip to view under the microscope You should be able to see the fungi well under 100X and 400X The actinomycetes can be heatfixed and gramstained to view under oil immersion at 1000X Light (also known as compound) microscopes, can see microbes at much finer resolution and have higher magnification powerWhen samples of a food are placed on a microscope slide and viewed under a light microscope, one can observe the cellular structures of the microbial community present




The Fungi Kingdom Mycology The Study Of Fungi



Microscopy Of Spores Hyphae Cystidia Trama To Identify Fungi
Lichen and fungi under microscope Colonies of mold fungi cultivated from indoor air Liquefactive necrosis of the human brain, light photomicrograph Word writing text H1N1 Business concept for Swine flu Respiratory disease most common caused by influenza virusesFungi under microscope Overview In this simulation, you will use microscopy to observe, identify, and classify examples of varied prokaryotic and eukaryotic microorganisms Bacteria Algae – Spirogyra Protozoa – Amoeba Fungi – Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast) and Aspergillus (mold) There are three factors that determine the quality of a microscopic image While that was the catalyst for following this area of study, it wasn't his only reason Under the supervision of Jones and Professor Lilian Vrijmoed during Pang's PhD he found his own inspiration "While studying the phylogeny of marine fungi, and looking at them under the microscope, I found that they were very beautiful," he says
.jpg)



Superficial Mycoses
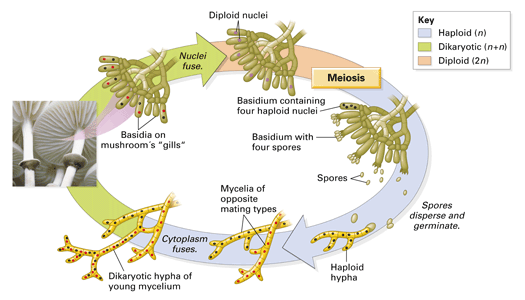



Chapter 18 Concept 18 2
Under the microscope, it should now be possible to see any of the important characteristics which will be used for identification These include the spores, acsi (sacs containing the spores), paraphyses (infertile structures between the asci), hairs, and the structure of the exterior of the fungus
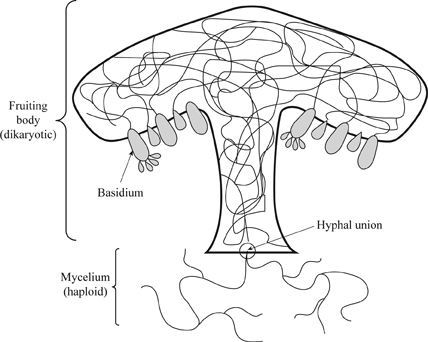



Definition Of The Major Groups Of Fungi Chegg Com



1




Fungi Microbiology



Microscopy Of Spores Hyphae Cystidia Trama To Identify Fungi



Fungus Wikipedia
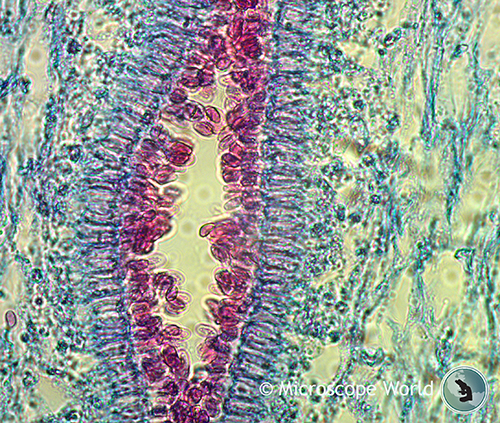



Mushrooms Under The Microscope
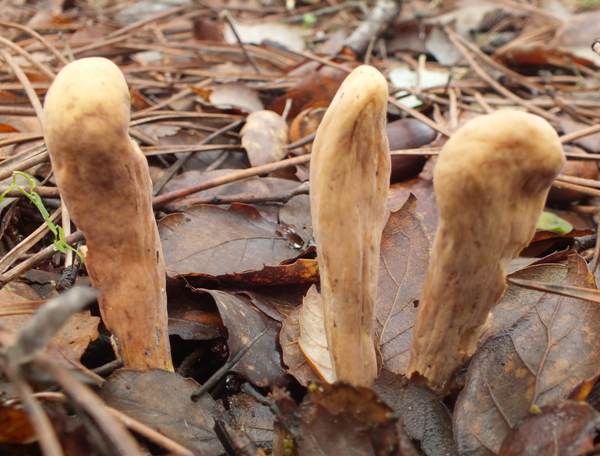




Clavariadelphus Pistillaris Giant Club Fungus Identification



Characteristics Of Fungi Biology Ii




A Text Book On Diseases Of The Ear Nose And Throat Ike The Tendrils Of A Running Vine If A Bit Of Deposit Be Torn Ofi Teased In Glycerin And Examined Witha




The Many Kinds Of Fungi



Basidiomycota
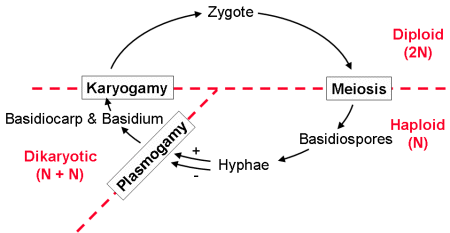



Reading Fungi Biology Ii Laboratory Manual




The Kingdom Fungi These Morels Are A Type Of Fungus Prized By Many People For Their Distinctive Flavor Unlike The Violets Fungi Are Not Plants And Do Ppt Download




Fungi Protist Prezi By Nini Ho



Fungus Microscopic View Of S Free Stock Photos Rgbstock Free Stock Images Hisks February 13 10 11
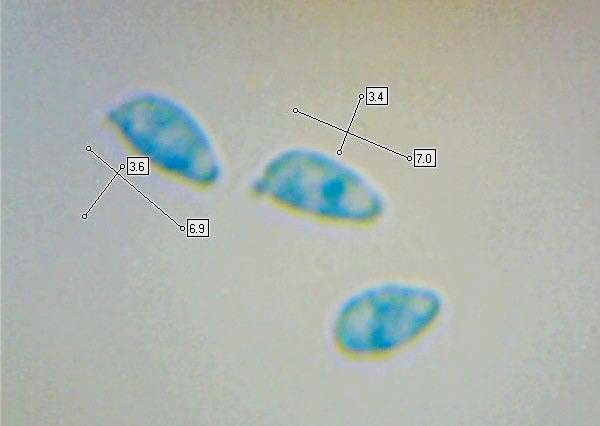



Clavulinopsis Laeticolor Handsome Clubfungus
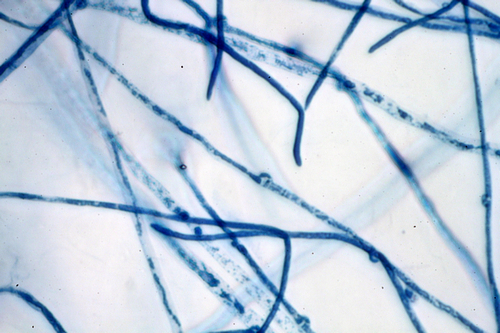



Club Fungi




24 3c Ascomycota The Sac Fungi Biology Libretexts




Club Fungi Microscopic Photography Fungi Abstract



2



Nick Baker S Hidden Britain Pressreader
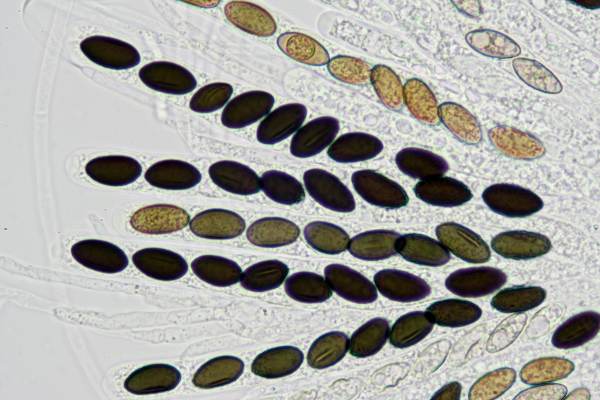



Microscopy Of Spores Hyphae Cystidia Trama To Identify Fungi




Basidiomycetes Club Fungi Coprinus Puccinia Graminis Microscope Slides Carolina Com




21 2 Classification Of Fungi Ppt Video Online Download




Tricophyton Tonsurans Varied Microconidia Of Teardrop Club Pencil And Balloon Shapes Borne Singularly Or In Clusters Balloon Shapes Science Lab Balloons
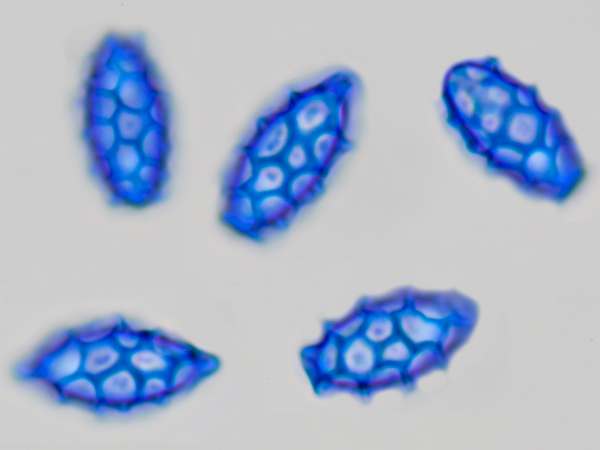



Microscopy Of Spores Hyphae Cystidia Trama To Identify Fungi




Reading Fungi Biology Libretexts
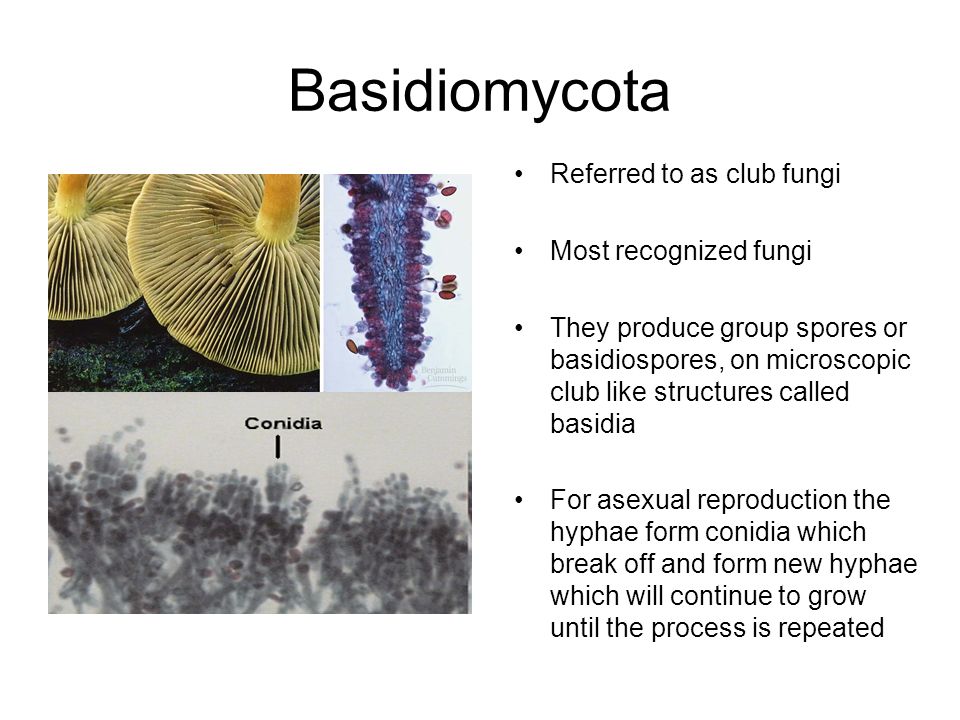



Kingdom Fungi Definition Ppt Video Online Download




Basidiomycota An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Microscopy Of Spores Hyphae Cystidia Trama To Identify Fungi



Classification Of Fungi Biology Ii




Pdf Clavariadelphus Pakistanicus Sp Nov A New Club Fungus Basidiomycota Gomphales From Himalayan Moist Temperate Forests Of Pakistan




Fungi Fungi Common Fungi Examples Mushrooms Yeasts Molds




Club Fungi Large Images




Observing Yeast Under The Microscope Microscope Club




16 3 Macrofungi Biology Libretexts




Reading Fungi Biology Ii Laboratory Manual



Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer Specialized Microscopy Techniques Differential Interference Contrast Image Gallery Mushroom Polyporus Fungus



Microscopic Volatile Spores Of Puffball Fungus Lycoperdon Basidiomycota Is A Genus Of Puffball Mushrooms Stock Image Image Of Fungi Particles




Fungi Algae Protozoa And Parasites Subject Pharmaceutical Microbiology



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes




Basidiomycota An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Classifications Of Fungi Biology For Majors Ii




Fungi Concepts Of Biology




A Rare Club Fungus In Old Grassland Violet Clavaria Zollingeri Stock Photo Alamy




Phylum Basidiomycetes The Club Fungi Or Chegg Com
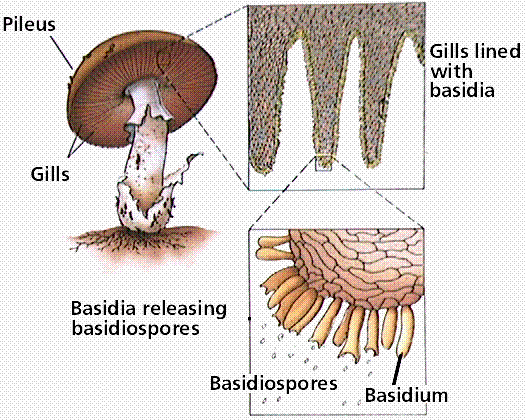



Phylum Basidiomycota The Basidiomycetes Club Fungi



Hillis2e Ch22



Fungi



Basidiomycota




Club Fungi Large Images




Club Bangahs Music Download Beatport




The Secret World Of Fungi The Wildlife Trust For Lancashire Manchester And North Merseyside



Classification And Importance Of Fungi



4 Fungi Laboratory Manual For Sci104 Biology Ii At Roxbury Community College
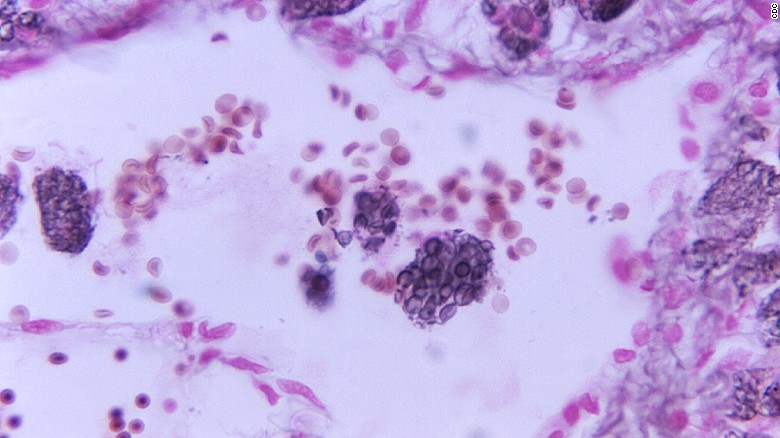



Fungal Diseases Under The Microscope
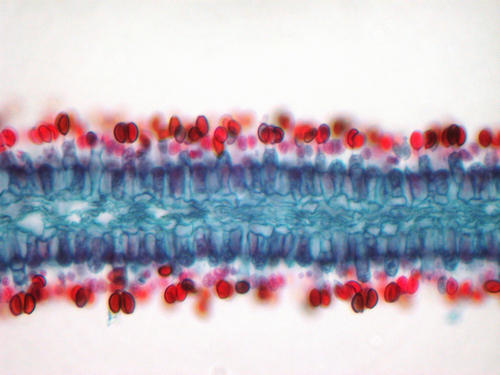



Club Fungi




Club Fungi Black And White Stock Photos Images Alamy




Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Biology For Majors Ii




Club Fungi Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




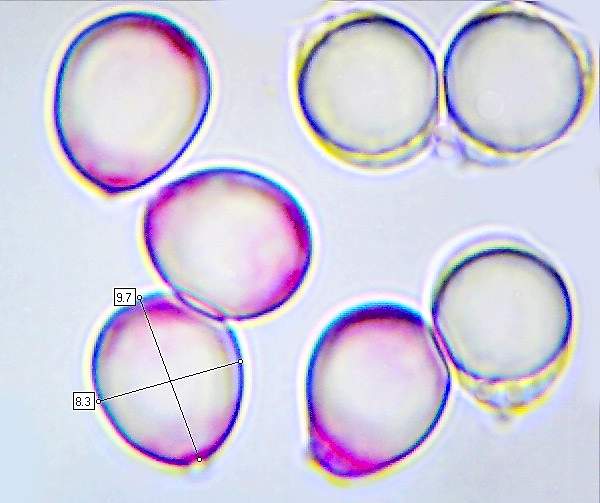
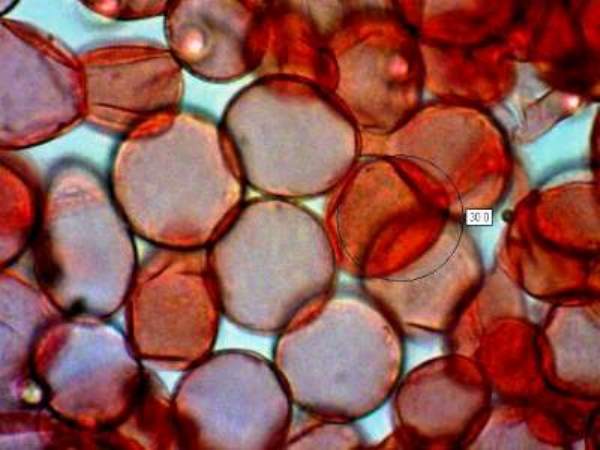
Microscopic Morphology Of Different Fungal Spores A T Download Scientific Diagram




Fungus Wikipedia



1




You Aren T Tripping Mushrooms And Fungi Are Taking Over Fashion Vogue



Club Fungi




Using A Microscope To Study Mushrooms Mushroomexpert Com



Bil 160 Lecture 18



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes
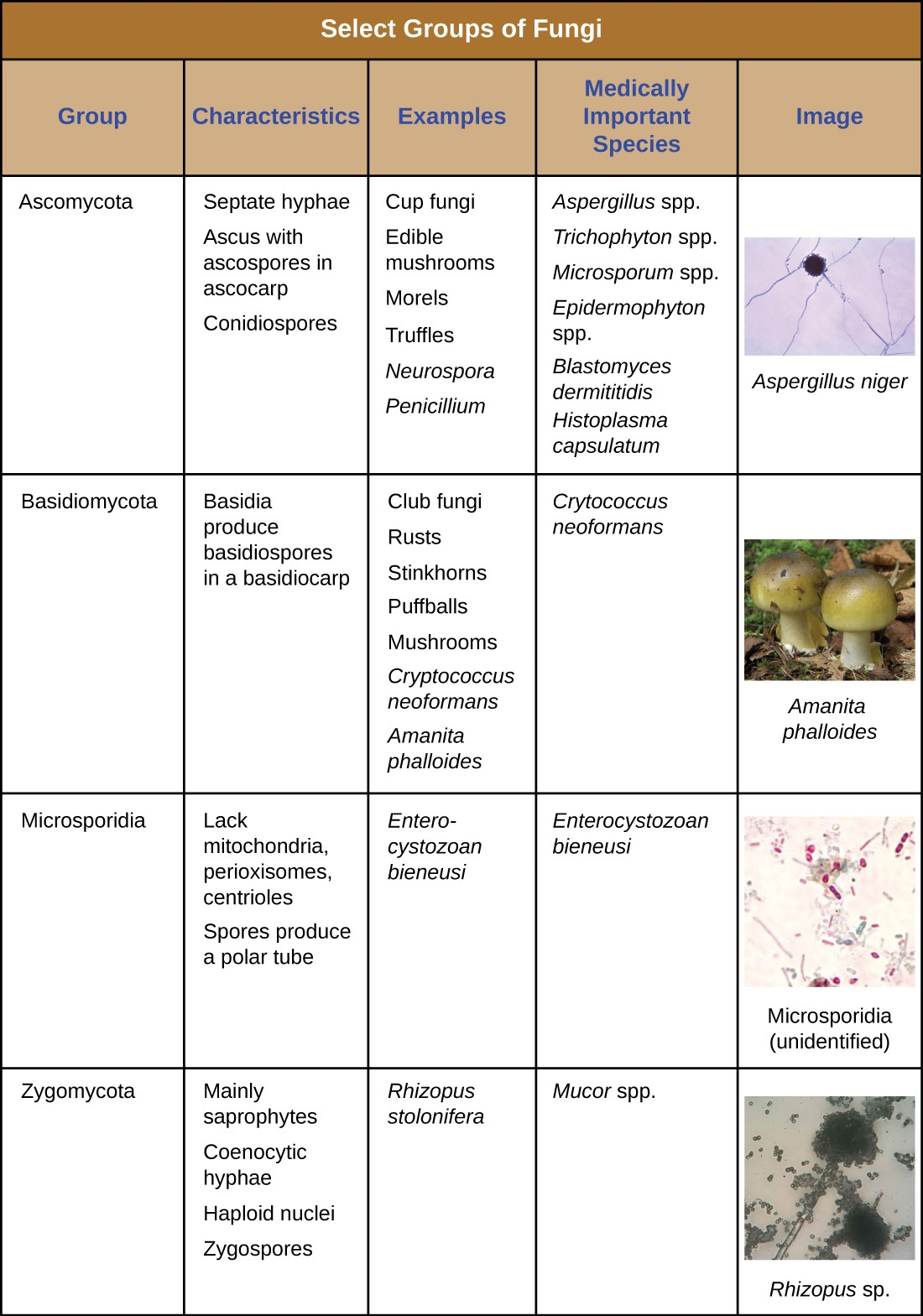



4 3 Fungi Allied Health Microbiology



1




Kingdom Fungi Continued Fungal Phyla 3 Phyla But




Fungi Apbio



Basidiomycota




Reading Fungi Biology Libretexts
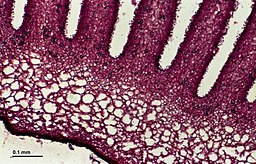



Kingdom Fungi Types Examples Morphology Structure And Importance




Fungi Microbiology
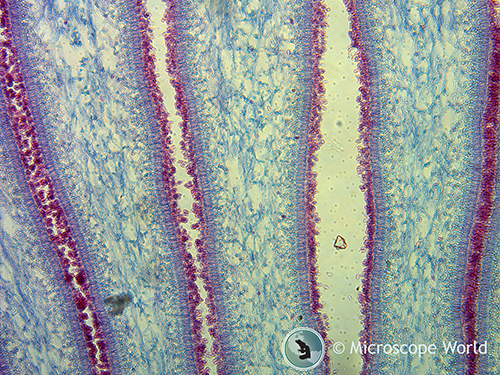



Mushrooms Under The Microscope
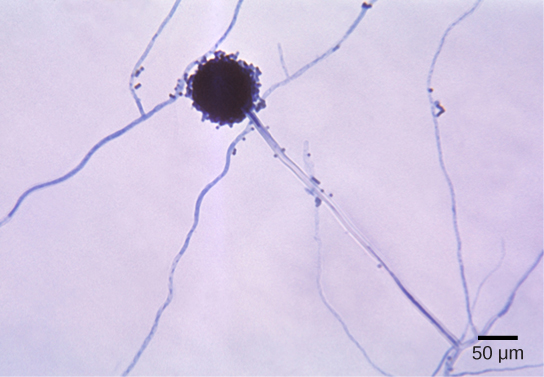



24 2 Classifications Of Fungi Biology Libretexts




47 Identifying Fungi Biology Libretexts




Classification Of Fungi Mycology Microbe Notes
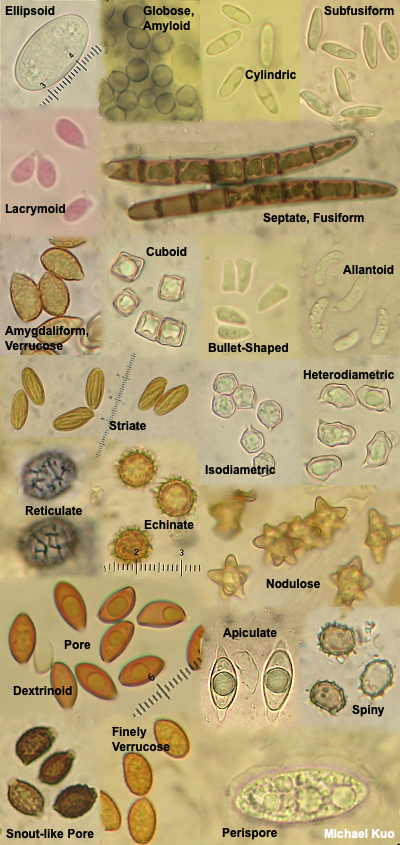



Using A Microscope To Study Mushrooms Mushroomexpert Com
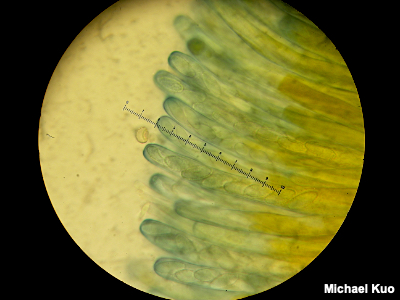



Using A Microscope To Study Mushrooms Mushroomexpert Com



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿